ESXi Ransomware Campaign | February 2023
Here's what you need to know.
Background
On February 3rd, 2023, reports emerged showing an extensive ransomware campaign targeting publicly exposed VMware ESXi servers. Researchers believe that the threat actors responsible are exploiting a two-year-old vulnerability, CVE-2021-21974. However, the specific vulnerability is not yet confirmed. VMware has publicly stated there is no evidence of a Zero-Day vulnerability, believing the flaw to be an old one for which some organizations remain unpatched. At the latest reporting, approximately 3,800 servers have been ransomed, roughly 300 of which are in the United States.
Early samples of the campaign, ESXiArgs, were only encrypting configuration files and leaving data relatively intact. This made recovery possible without paying the ransom for a decryptor. Later samples of the ransomware have evolved, making recovery more difficult. The impact and possibility of recovery will need to be evaluated.
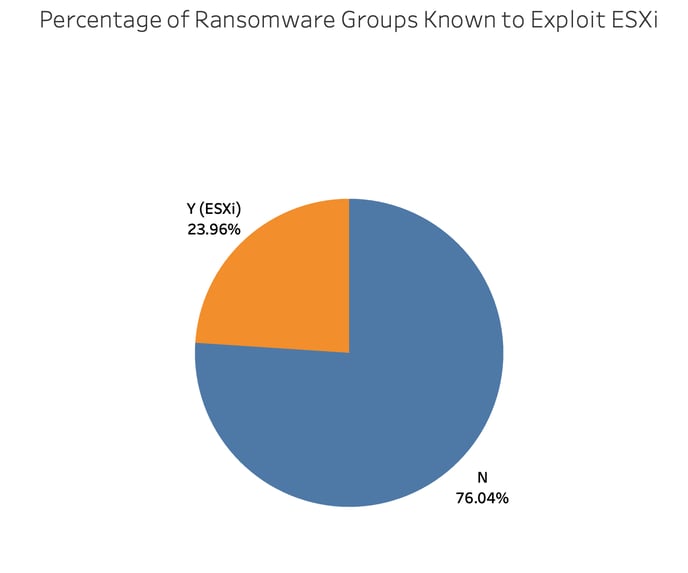
Based on Corvus Threat Intel data, nearly one-quarter of ransomware groups have leveraged ESXi servers as part of their attacks. This campaign is unique because threat actors are using ESXi servers as the point of entry into the network and systematically searching for publicly exposed vulnerable targets from the outset.
What is ESXi?
If you’ve ever heard of a “Virtual Machine” or “VM” this is essentially a computer within a computer. You can run a Windows operating system and have a separate VM running Linux. In order to function, this mini-computer needs to share resources with the primary operating system or other VMs. Each VM needs to have RAM, CPU, and storage resources to function but needs a way to know how to share these.
To properly manage the VM and share resources, there is something called a hypervisor to distribute these. ESXi is a hypervisor. It is essentially software that sits on a physical server and manages the resources to ensure the VMs under its jurisdiction can function properly.
Since hypervisors manage numerous VMs, they are an attractive target for ransomware actors. Attacking a single ESXi can disable all of the virtual machines underneath. Those virtual resources may have contained valuable data or housed applications or other infrastructure rendered unusable until recovery. This makes life for a threat actor much easier since they don’t have to discover and attack each virtual resource individually, instead one target can multiply their efforts.
In terms of market share for virtualization, the numbers may differ slightly depending on the firm doing the analysis. However, VMware is one of the top providers with ESXi specifically making up around 6%. It’s unclear whether these analyses rely on externally visible products or whether the methodology includes a way to track the internal assets of companies.
Next Steps
If you use ESXi at your organization, make sure it’s configured not to be publicly accessible from the internet. Threat actors continually scan for targets as part of this campaign, so don’t be one of them. Also, ensure your ESXi, vCenter, and other virtualization components are patched and up-to-date.
Resources
- ESXiArgs Ransomware Virtual Machine Recovery Guidance (CISA)
- Exploit Vector Analysis of Emerging ‘ESXiArgs’ Ransomware (GreyNoise)
- ESXiArgs Ransomware Hits Over 3,800 Servers as Hackers Continue Improving Malware (SecurityWeek)
- An Analysis of the VMware ESXi Ransomware Blitz (Intel471)
- How to secure your VMware ESXi hosts against ransomware (Truesec)
- Prevent Attackers From Taking Over ESXi 8.0 Hosts (Truesec)